1970 United Kingdom general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
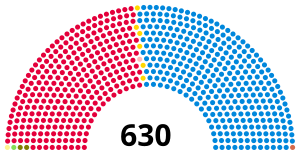
All 630 seats in the House of Commons 316 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 72.0% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
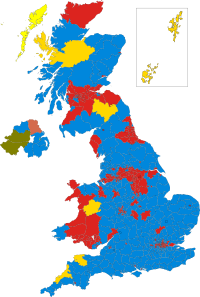 Colours denote the winning party—as shown in § Results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the House of Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1970 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 18 June 1970. It resulted in a surprise victory for the Conservative Party under leader Edward Heath, which defeated the governing Labour Party under Prime Minister Harold Wilson. The Liberal Party, under its new leader Jeremy Thorpe, lost half its seats. The Conservatives, including the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP), secured a majority of 30 seats. This general election was the first in which people could vote from the age of 18, after passage of the Representation of the People Act the previous year, and the first UK election in which party affiliations of candidates were put on the ballots.[1]
Most opinion polls prior to the election indicated a comfortable Labour victory, and put Labour up to 12.4% ahead of the Conservatives. On election day, however, a late swing gave the Conservatives a 3.4% lead and ended almost six years of Labour government, although Wilson remained leader of the Labour Party in opposition. Writing in the aftermath of the election, the political scientist Richard Rose described the Conservative victory as "surprising" and noted a significant shift in votes between the two main parties.[2] The Times journalist George Clark wrote that the election would be "remembered as the occasion when the people of the United Kingdom hurled the findings of the opinion polls back into the faces of the pollsters".[3]
The result would provide the mandate for Heath as Prime Minister to begin formal negotiations for the United Kingdom to become a member state of the European Communities (EC)—or the "Common Market" as it was more widely known at the time, before it later became the European Union; the UK officially joined the EC on 1 January 1973, along with the Republic of Ireland and Denmark.
Frontbench Labour politicians George Brown and Jennie Lee were voted out at this election.
This marked the end of a series of elections where both main parties won over 40% of the vote. This would not occur again for the Conservatives for nine years; Labour would wait 27.
The result was cast as a two-party politics outcome, with no third party reaching 10% of the (total) vote. Such an outcome would not happen again until the 2017 election.
The election was the last in which a nationwide UK party gained seats in Northern Ireland.[4] The UUP sat with the Conservative Party at Westminster, traditionally taking the Conservative parliamentary whip. To all intents and purposes the UUP functioned as the Northern Ireland branch of the Conservative Party. However, hardline unionist Ian Paisley unseated the UUP incumbent in North Antrim, a clear sign that the UUP's complete dominance over unionist politics in Northern Ireland was already starting to weaken. In 1972, in protest over the permanent prorogation of the Parliament of Northern Ireland, Westminster UUP MPs withdrew from the alliance.[5][page needed]
Election date
[edit]The date of 18 June was supposedly chosen because Harold Wilson wanted as Prime Minister to go to the polls before the introduction of decimal coinage in early 1971, for which his government had been responsible and which he thought was hugely unpopular,[6][page needed] and because Wilson sought to gain some momentum by surprising the Conservatives, who were expecting an October election.[6][page needed]
Overview
[edit]Commentators believed that an unexpectedly bad set of balance of payments figures (a £31-million trade deficit) published three days before the election and a loss of national prestige after the England football team's defeat by West Germany on 14 June in the World Cup contributed to the Labour defeat.[7]

Other factors that were cited as reasons for the Conservative victory included union indiscipline, rising prices, the risk of devaluation, the imposition of Selective Employment Tax (SET), and a set of jobless figures released on final week of the campaign showing unemployment at its highest level since 1940. Interviewed by Robin Day, the outgoing Prime Minister Harold Wilson highlighted the possibility that "complacency engendered by the opinion polls" may have resulted in a poor turnout of Labour supporters.[8]
As defending world champions, England's venture in the World Cup attracted a much keener public interest than the general election did.[9] However an analysis by pollster Matt Singh for the 50th anniversary of the election concluded that the late swing had been caused by the weak economic data and that there was "no evidence" that the World Cup had influenced the outcome.[10]
American pollster Douglas Schoen and Oxford University academic R. W. Johnson asserted that Enoch Powell had attracted 2.5 million votes to the Conservatives, although the Conservative vote only increased by 1.7 million. Johnson later stated "It became clear that Powell had won the 1970 election for the Tories ... of all those who had switched their vote from one party to another, 50 per cent were working class Powellites".[11] The Professor of Political Science Randall Hansen assessed a range of studies, including some which contended that Powell had made little or no difference to the result, but concluded that "At the very least, Powell's effect was likely to have fired up the Conservative vote in constituencies which would have voted Tory in any event".[12][page needed] Election night commentators Michael Barratt and Jeffrey Preece dismissed any special "Powell factor", as did Conservative MPs Reginald Maudling, Timothy Raison and Hugh Dykes.[8]
The 1970–74 Parliament has to date been the only time since the 1924–29 Parliament in which the Conservative Party were only in government for one term before returning to opposition.
The most notable casualty of the election was George Brown, deputy leader of the Labour Party, who lost to the Conservative candidate in the Belper constituency. Brown had held the seat since 1945. Labour Minister for the Arts, Jennie Lee lost her Cannock seat, held by Labour since 1935 on a swing of 10.7% to the Conservatives in what Richard Rose called "the biggest upset" of the election.[13]
Unusually for the Liberal Party, the by-elections between 1966 and 1970 had proved almost fruitless, with many Liberal candidates losing deposits. The one exception was its by-election gain of Birmingham Ladywood in June 1969; this was promptly lost in the 1970 general election. The party found itself struggling to introduce its new leader Jeremy Thorpe to the public, owing to the extensive coverage and attention paid to Enoch Powell. The election result was poor for the Liberals, with Thorpe only narrowly winning his own seat in North Devon.[7] Indeed, of the six MPs returned, three (Thorpe, David Steel and John Pardoe) were elected by a majority of less than 1,000 votes.[14]
The BBC's election coverage was led by Cliff Michelmore, along with Robin Day, David Butler and Robert McKenzie.[7] There were periodic cutaways to the BBC regions. This coverage has been rerun on BBC Parliament on several occasions, including on 18 July 2005 as a tribute to Edward Heath after his death the previous day. Its most recent screening was on the 20th of June 2020, to commemorate the 50th anniversary of its first transmission.[15] The BBC coverage was parodied by Monty Python's Flying Circus in its famous "Election Night Special" sketch.
Both BBC and ITN carried their 1970 election night broadcasts in colour, although segments broadcast from some remote locations and some BBC and ITN regional bureaus were transmitted in black-and-white. Some ITV regions were not yet broadcasting in colour at the time of the 1970 elections.
The right to vote in this election was widened by the Labour government's Sixth Reform Act, which reduced the voting age from 21 to 18 years. The United Kingdom was the first major democratic nation to extend suffrage to this age group.[16][17][18] Case law subsequently established the right for undergraduate students to vote in the constituency of their university. This followed an appeal to the High Court.[19]
Timeline
[edit]The Prime Minister, Harold Wilson, visited Buckingham Palace on 18 May and asked the Queen to dissolve Parliament on 29 May, announcing that the election would be held on 18 June. The key dates were as follows:
| Friday 29 May | Dissolution of the 44th Parliament and campaigning officially begins |
| Monday 8 June | Last day to file nomination papers |
| Wednesday 17 June | Campaigning officially ends |
| Thursday 18 June | Polling day |
| Friday 19 June | The Conservative Party wins power with a majority of 31 |
| Monday 29 June | 45th Parliament assembles |
| Thursday 2 July | State Opening of Parliament |
Opinion poll summary
[edit]Summary of the final polling results before the general election.[20]
| Party | Marplan | Gallup | National opinion polls (NOP) | Opinion Research Centre (OPC) | Harris | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 41.5% | 42.0% | 44.1% | 46.5% | 46.0% | |
| Labour | 50.2% | 49.0% | 48.2% | 45.5% | 48.0% | |
| Liberal | 7.0% | 7.5% | 6.4% | 6.5% | 5.0% | |
| Other parties | 1.3% | 1.5% | 1.3% | 1.5% | 1.0% | |
| Labour lead | 8.7% | 7.0% | 4.1% | −1.0% | 2.0% | |
| Fieldwork dates | 11–14 June | 14–16 June | 12–16 June | 13–17 June | 20 May – 16 June | |
| Sample size | 2,267 | 2,190 | 1,562 | 1,583 | 4,841 | |
Results
[edit]This was the first general election where 18-year-olds had the right to vote. Therefore, despite 1.1 million more people voting in 1970 compared to 1966, turnout actually fell by 3%. This 72% turnout was the lowest since the 1935 general election and compared with a post-War high of 84% in 1950. Professor Richard Rose described the low turnout, which he noted was "one of the lowest since the introduction of the democratic franchise", as surprising to politician and pollsters. Changes to electoral law as part of the Representation of the People Act 1969 had made postal voting easier and polling stations were open an hour later than in past elections, and this would have been expected to improve turnout. On top of this it was reported by Rose that an estimated 25% of 18- to 21-year-olds who were now eligible to vote had not put their names on the electoral register, meaning the turnout was even lower than the percentage figure suggested. Rose also argued that the turnout figures in Britain were "now among the lowest in the Western world."[2] Because the previous election had been in 1966, some people had not had their chance to vote in a general election until the age of 25. Labour's number of votes, 12.2 million, was ironically the same amount they had needed to win in 1964. The Conservative vote surge cost Labour in many marginal seats. Rose suggested the absolute fall in the number of Labour votes suggested that many of the party's supporters had decided to abstain. He also noted that the Labour Party's local organisation was poorer than that of the Conservatives, but did not feel this was a significant factor in Labour supporters failing to come out to vote for the Party given that this organisational difference had been the case in past elections without having this effect.[2] For the Liberals, a small 1% drop in their vote share saw them lose 6 seats, 3 of which were held by the narrowest of margins.
In the end the Conservatives achieved a swing of 4.7%, enough to give them a comfortable working majority. As for the smaller parties, they increased their number in the Commons from 2 to 6 seats.
The Scottish National Party won its first ever seat at a general election (they had won several by-elections previously, going back as far as 1945), although they did lose Hamilton, which they won in a by-election in 1967.
| Candidates | Votes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Leader | Stood | Elected | Gained | Unseated | Net | % of total | % | No. | Net % | |
| Conservative | Edward Heath | 628 | 330 | 80 | 3 | +77 | 52.4 | 46.4 | 13,145,123 | +4.5 | |
| Labour | Harold Wilson | 625 | 288[note 1] | 1 | 77 | −76 | 45.7 | 43.1 | 12,208,758 | −4.9 | |
| Liberal | Jeremy Thorpe | 332 | 6 | 0 | 6 | −6 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 2,117,035 | −1.0 | |
| SNP | William Wolfe | 65 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +1 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 306,802 | +0.6 | |
| Plaid Cymru | Gwynfor Evans | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 175,016 | +0.4 | ||
| Unity | N/A | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | +2 | 0.3 | 0.50 | 140,930 | N/A | |
| Independent | N/A | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 39,264 | 0.0 | ||
| Communist | John Gollan | 58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 37,970 | −0.1 | ||
| Protestant Unionist | Ian Paisley | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 35,303 | N/A | |
| Republican Labour | Gerry Fitt | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 30,649 | N/A | |
| Independent Labour | N/A | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 24,685 | +0.1 | |
| Ind. Conservative | N/A | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 24,014 | +0.1 | ||
| Democratic Party | Desmond Donnelly | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 15,292 | N/A | ||
| National Democratic | David Brown | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 14,276 | N/A | ||
| National Front | John O'Brien | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 11,449 | N/A | ||
| National Democratic | Gerry Quigley | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 10,349 | N/A | ||
| Vectis National Party | R. W. Cawdell | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1,607 | N/A | ||
| Independent Liberal | N/A | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1,456 | 0.0 | ||
| World Government | Gilbert Young | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1,016 | N/A | ||
| Mebyon Kernow | Len Truran | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 960 | N/A | ||
| Ind. Labour Party | Emrys Thomas | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 847 | 0.0 | ||
| British Movement | Colin Jordan | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 704 | N/A | ||
| Independent Progressive | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 658 | N/A | |||
| Socialist (GB) | N/A | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 376 | 0.0 | ||
| Young Ideas | Screaming Lord Sutch | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 142 | N/A | ||
| British Commonwealth | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 117 | N/A | |||
| Government's new majority | 30 |
| Total votes cast | 28,305,534 |
| Turnout | 72% |
Votes summary
[edit]Seats summary
[edit]Televised declarations
[edit]These declarations were covered live by the BBC where the returning officer was heard to say "duly elected".
| Constituency | Winning party 1966 | Constituency result by party | Winning party 1970 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | Lab | Lib | Others | |||||
| Guildford | Conservative | 27,203 | 13,108 | 8,822 | Conservative hold | |||
| Cheltenham | Conservative | 22,823 | 14,213 | 8,431 | Conservative hold | |||
| Salford West | Labour | 14,310 | 16,986 | Labour hold | ||||
| Wolverhampton North East | Labour | 15,358 | 17,251 | 1,592 | Labour hold | |||
| Salford East | Labour | 9,583 | 15,853 | 3,000 | Labour hold | |||
| Wolverhampton South West | Conservative | 26,252 | 11,753 | 2,459 | 318 | Conservative hold | ||
| Newcastle upon Tyne Central | Labour | 4,256 | 13,671 | 1,433 | Labour hold | |||
| Newcastle upon Tyne North | Conservative | 15,978 | 12,518 | Conservative hold | ||||
| Exeter | Labour | 21,680 | 20,409 | 6,672 | Conservative gain | |||
| North Devon | Liberal | 18,524 | 5,268 | 18,893 | 175 | Liberal hold | ||
| West Aberdeenshire | Liberal | 18,396 | 6,141 | 12,847 | 2,112 | Conservative gain | ||
Incumbents defeated
[edit]See also
[edit]- List of MPs elected in the 1970 United Kingdom general election
- 1970 United Kingdom general election in Northern Ireland
- 1970 United Kingdom local elections
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b The seat and vote count figures for Labour given here include the Speaker of the House of Commons
- ^ The Conservative figure includes eight Ulster Unionists, and the Labour figure includes seven Northern Ireland Labour Party candidates.
References
[edit]- ^ HC Deb 10 December 1968 vol 775 cc242-87
- ^ a b c Richard Rose (1970). "Voting Trends Surveyed". The Times Guide to the House of Commons 1970. London: Times Newspapers Limited. p. 31.
- ^ George Clark (1970). "The General Election Campaign, 1970". The Times Guide to the House of Commons 1970. London: Times Newspapers Limited. p. 26.
- ^ Keohane, Dan (2000), Security in British Politics 1945–99, p. 183
- ^ Bell, Stuart; Seldon, Anthony, The Heath Government 1970–74: A Reappraisal
- ^ a b Haines, Joe (2003), Glimmers of Twilight, London: Politico's Publishers
- ^ a b c "1970: Heath's surprise victory", BBC News, 5 April 2005, retrieved 31 May 2018
- ^ a b BBC Election Results Programme, 18–19 July 1970
- ^ "Heath: The victory few predicted", BBC News, retrieved 31 May 2018
- ^ "Did England's World Cup defeat win the 1970 election for the Tories?". CapX. 19 June 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Heffer, Simon (1999), Like the Roman: The Life of Enoch Powell, London: Phoenix, p. 568
- ^ Hansen, Randell (2000), Citizenship and Immigration in Post-War Britain, Oxford University Press
- ^ Richard Rose (1970). "Voting Trends Surveyed". The Times Guide to the House of Commons 1970. London: Times Newspapers Ltd. p. 31.
- ^ The Times Guide to the House of Commons 1970. London: Times Newspapers Ltd. 1970. p. 250.
- ^ BBC Election 1970, BBC Parliament, archived from the original on 25 October 2010
- ^ Loughran, Thomas; Mycock, Andrew; Tonge, Jonathan (3 April 2021). "A coming of age: how and why the UK became the first democracy to allow votes for 18-year-olds". Contemporary British History. 35 (2): 284–313. doi:10.1080/13619462.2021.1890589. ISSN 1361-9462. S2CID 233956982.
- ^ Loughran, Thomas; Mycock, Andrew; Tonge, Jonathan (3 November 2021). "Lowering the voting age: three lessons from the 1969 Representation of the People's Act". British Politics and Policy at LSE. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ Bingham, Adrian (25 June 2019). "'The last milestone' on the journey to full adult suffrage? 50 years of debates about the voting age". History & Policy. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ Stephen D. Fisher & Nick Hillman. "Do students swing elections? Registration, turnout and voting behaviour among full-time students" (PDF). HEPI. p. 4.
- ^ Abrams, M. (1970), "The Opinion Polls and the 1970 British General Election", The Public Opinion Quarterly, 34 (2): 317–324, doi:10.1086/267808
Further reading
[edit]- Butler, David E.; et al. (1971), The British General Election of 1970, the standard scholarly study.
- Craig, F. W. S. (1989), British Electoral Facts: 1832–1987, Dartmouth: Gower, ISBN 0900178302
External links
[edit]- United Kingdom election results—summary results 1885–1979 Archived 23 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine
Manifestos
[edit]- A Better Tomorrow, 1970 Conservative Party manifesto
- Now Britain's strong – let's make it great to live in, 1970 Labour Party manifesto
- What a Life!, 1970 Liberal Party manifesto




